Innovative
products
The way we produce our alloys is driven by innovation and R&D. Continuous improvement and a “thinking outside the box” mentality are part of our daily business.
Our innovative products, tailored to our customers’ needs, are created by engaged people and come with a high level of service.
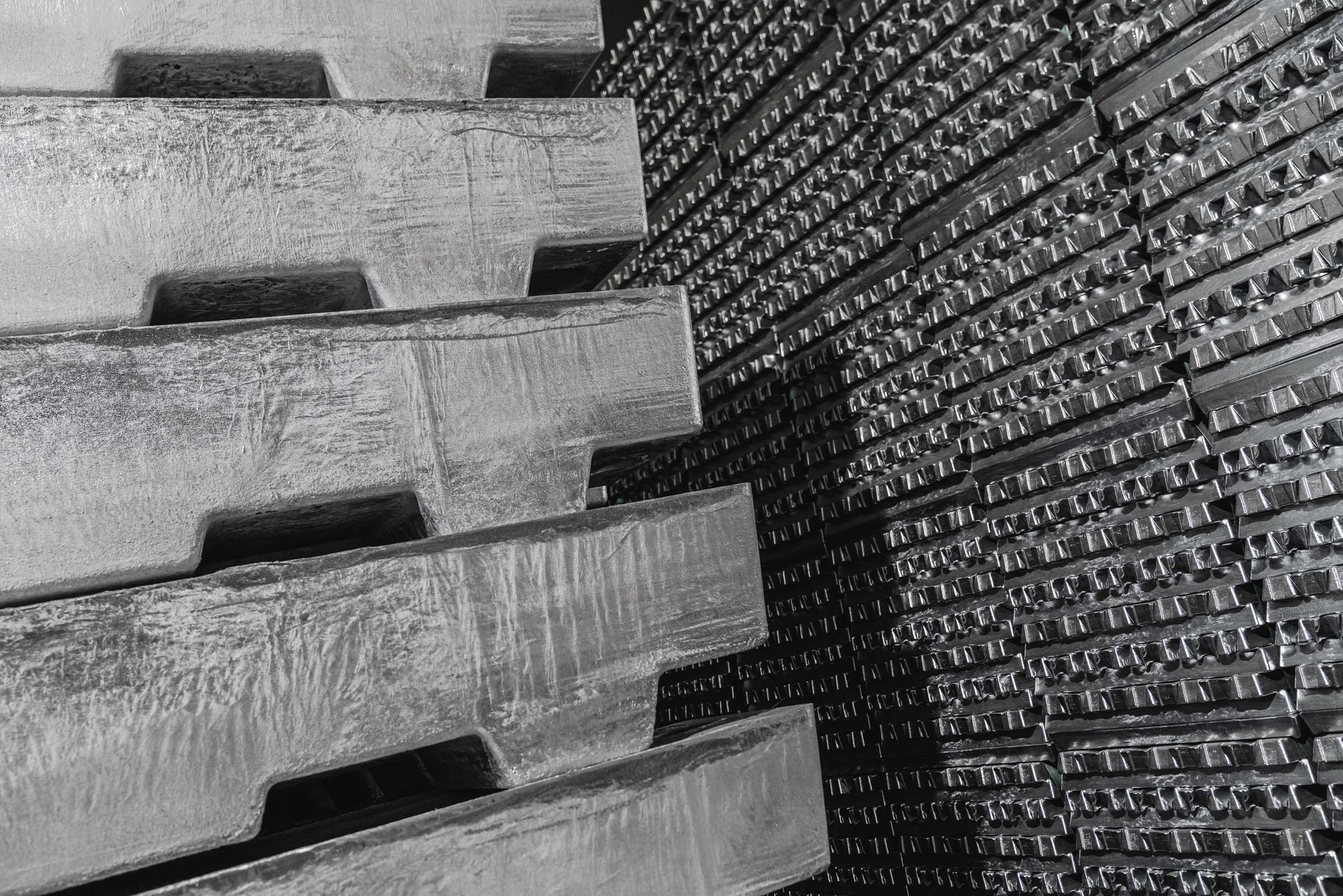
Our shapes for zinc die-casting foundries

(ca. 8,5 kg)

(ca. 8,5 kg)

(ca. 725 kg)
Our shapes for continuous- and batch-galvanizers

(ca. 1.800 kg)

(ca. 1.000 kg)
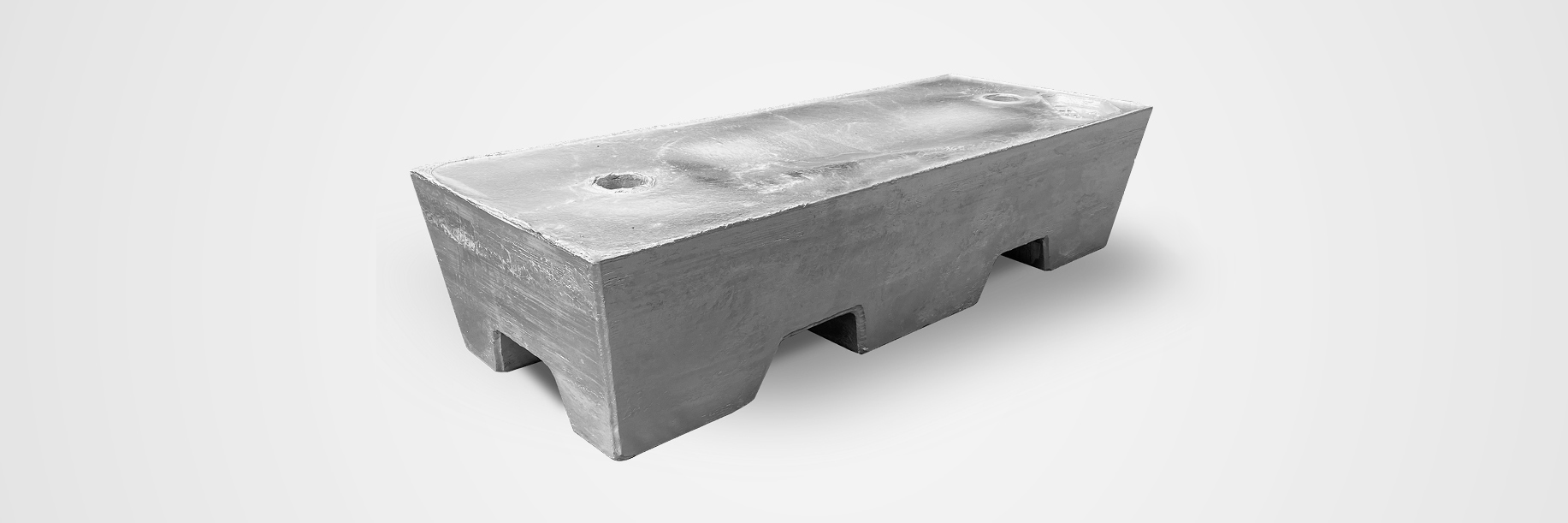

(ca. 1.300 kg)
casting
alloys
Die casting alloys represent roughly 12% of the zinc use worldwide. They are generally referred to as ZAMAK. It is an acronym for the German names of the metals of which the alloys are composed: Zink (Zn), Aluminium (Al), Magnesium (Mg) and Kupfer (Cu). The main alloys were developed by The New Jersey Zinc Company in 1929.
our casting alloys
Today Zamak 3 (ZnAl4/ZL0400), Zamak 5 (ZnAl4Cu1/ZL0410) and Zamak 2 (ZnAl4Cu3/ZL0430) are the most commonly used die casting alloys.
REAZN can also supply Zamak 6 (ZnAl6Cu1/ZL0610), Zamak 8 (ZnAl8Cu1/ZL0810), Zamak 12 (ZnAl11Cu1/ZL1110), Zamak 27 (ZnAl27Cu2/ZL2720) which are suited for gravity casting applications.
Furthermore REAZN UK holds a license agreement for the manufacturing and selling of the EZAC™ high creep resistant alloy.
fields of application
From building and furniture fittings to automotive components, zinc die castings positively impact our lives on a daily basis. A variety of casting processes are available to economically manufacture cast parts of whatever size and quantity required. Besides this, zinc die casting offers numerous advantages compared to other production methods: dimensional stability, precise casting tolerances, moderate casting temperatures, superior casting fluidity, reduced machining, thermal and electrical conductivity, faster production rates, extended tool life, well suited for coating and many more.
Examples of die cast parts: cam locks and fixing dowels, coffee machines, mirror frames, electrical connectors, zippers, bathroom fixtures (faucets and shower heads), safety razors, handles, locks, hinges and antenna holders in cars, golf clubs or wheel balancing weights.
galvanizing
alloys
One of zinc’s most exceptional qualities is its natural capacity to protect steel from corrosion. When left unprotected, steel will corrode in almost any environment. Zinc coatings protect steel by providing a physical barrier for the underlying steel. Protecting steel against corrosion is the most important market for zinc, representing 55 – 60% of zinc use worldwide.
our galvanizing alloys
Starting from a zinc (Zn) base, alloying elements like aluminium (Al), Nickel (Ni) or Magnesium (Mg), can be added to produce galvanized coatings with different properties.
The most common galvanizing alloys are made in a wide range of compositions from 5 – 40 % Aluminium (Galva alloys). With the addition of rare earths, these alloys are then called Galfan alloys.
ZnNi and/or ZnNiBi alloys are still added to their baths by many general galvanizers, whereas ZnAlMg is an alloy family mainly used in continuous galvanizing.
As no standards apply for this type of uses, we are flexible and can produce customized alloys with tailor made specifications.
fields of application
General Galvanizing is also known as Hot Dip Galvanizing or Batch Galvanizing. The process refers to the galvanizing of previously fabricated or manufactured steel items. The fabricated steel article is cleaned and then dipped into a molten zinc bath, either on racks for small items or individually for large items. Examples include steel grating, guard rails, light posts or agricultural machinery.
Continuous Galvanizing: In the continuous hot-dip galvanizing process, steel strip is fed into a molten zinc bath at speeds up to 200 meters per minute. Continuously galvanized coatings are metallurgically bonded to the steel they protect. This ensures coating adhesion critical for manufacturing processes that bend, stamp, roll or draw the steel into its final product shape. Examples include car bodies, white goods, corrugated sheet metal or steel roofing.
